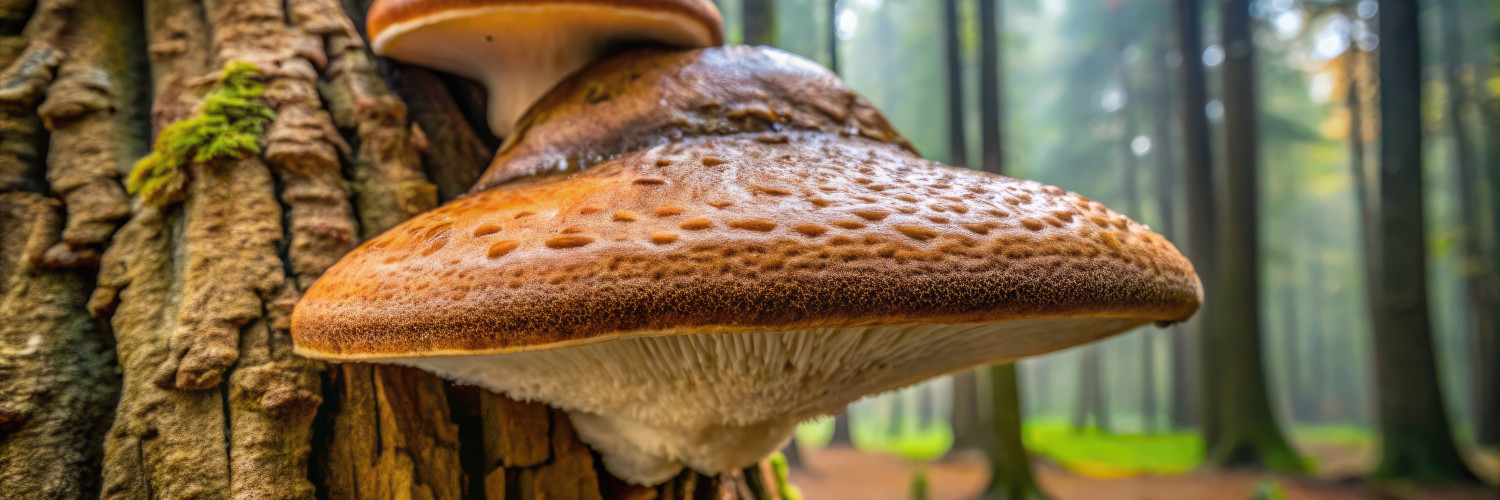
Phellinus linteus, commonly known as Sanghuang, Meshimakobu, or Black Hoof Mushroom, is a medicinal fungus in the family Hymenochaetaceae. Recognized for its therapeutic potential in East Asian traditional medicine, this mushroom has gained attention in modern scientific studies for its bioactive compounds and diverse benefits.
Botanical Characteristics
Phellinus linteus is a wood-decaying polypore fungus characterized by its dark, hoof-shaped fruiting body, which adheres firmly to the surface of trees. The fruiting body has a tough, woody texture, and its upper surface is often brown to black with a velvety or cracked appearance. The pore surface underneath is yellow to brown, composed of tiny, circular pores. This mushroom is slow-growing and develops on hardwoods, particularly mulberry trees, making it distinct in its ecological niche.
Chemical Composition
The bioactivity of Phellinus linteus is attributed to its diverse chemical constituents, including polysaccharides, triterpenoids, phenolic compounds, and flavonoids. These compounds exhibit antioxidant, immunomodulatory, and adaptogenic properties. Key bioactive components, such as beta-glucans, are linked to its ability to support immune function, while triterpenoids are studied for their potential in maintaining cellular balance and promoting wellness.
Habitat and Growth
Native to East Asia, Phellinus linteus thrives in warm, temperate regions. It typically grows on decaying hardwoods, especially mulberry (Morus spp.), and is less commonly found on other hardwood species. It favors shaded, humid environments and is often located in old forests. Cultivation efforts have expanded its availability, with controlled growth on sawdust or natural wood substrates replicating its natural conditions.
Historical and Modern Uses
Historically, Phellinus linteus has been a staple in Chinese, Japanese, and Korean traditional medicine, where it was used to promote vitality and balance. It was often prepared as a decoction or powder, valued for its perceived ability to fortify the body. In modern times, the mushroom is extensively studied for its therapeutic potential, particularly its role in supporting the immune system and cellular health. While avoiding claims of curing or treating specific diseases, Phellinus linteus is now incorporated into dietary supplements and functional foods for general wellness.
Body Systems Supported by Phellinus linteus Mushroom:
- Immune System
- Digestive System
- Respiratory System
- Cardiovascular System
- Skin and Cellular Health
- Nervous System
- Endocrine System
Phellinus linteus Substances and the Immune System:
Phellinus linteus, a medicinal mushroom, is renowned for its ability to enhance and regulate immune function through a synergistic blend of bioactive compounds, vitamins, and minerals. Its polysaccharides, triterpenoids, phenolic acids, and trace minerals work in harmony to support the immune system by activating cellular defenses, balancing immune responses, and protecting immune cells from oxidative stress.
Key bioactive compounds such as beta-glucans, found in polysaccharides, bind to pattern recognition receptors (PRRs) on immune cells, including macrophages and dendritic cells. This interaction initiates the production of cytokines, which activate natural killer (NK) cells, T cells, and other components of the immune system, enhancing both innate and adaptive immunity. By improving immune cell communication and mobilization, beta-glucans enhance the body's ability to detect and respond to external threats.
The triterpenoids in Phellinus linteus contribute to immune balance by modulating inflammatory pathways. These compounds regulate the production of pro-inflammatory and anti-inflammatory mediators, ensuring the immune response is effective without causing tissue damage. Simultaneously, phenolic compounds act as powerful antioxidants, neutralizing free radicals and protecting immune cells from oxidative stress, a key factor that can impair immune function under challenging conditions.
Trace minerals such as selenium and zinc play a vital role in the enzymatic activities required for immune cell replication, repair, and defense mechanisms. These minerals also support the production of antioxidants like glutathione, which shields immune cells from environmental damage. Additionally, ergosterol, a precursor to vitamin D, supports the differentiation of T cells and the production of antibodies, enhancing adaptive immune responses.
Scientific Articles on the Topic:
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9410671/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC8547106/
https://trialsjournal.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s13063-021-05740-5
Phellinus linteus Substances and Digestive System:
The polysaccharides, particularly beta-glucans, serve as prebiotics, nourishing beneficial gut bacteria such as Lactobacillus and Bifidobacterium. This fosters a balanced microbiome, essential for efficient digestion and nutrient absorption. These compounds also encourage the production of short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs) in the colon, which help maintain intestinal integrity and overall gut health. The dietary fiber-like properties of polysaccharides aid in regular bowel movements by promoting water retention and smooth intestinal motility.
Triterpenoids contribute to digestive wellness by modulating natural inflammatory pathways, reducing irritation, and soothing the gastrointestinal tract. Phenolic acids, with their potent antioxidant properties, neutralize free radicals in the digestive system, preventing oxidative stress that can damage gut cells and impair enzymatic functions. These antioxidants, combined with trace minerals like selenium and zinc, support the repair and maintenance of the intestinal barrier, ensuring its strength and minimizing permeability.
The mushroom’s natural detoxifying properties enhance the body’s ability to eliminate toxins from the digestive tract, reducing the burden on the liver and kidneys. By binding to harmful substances in the gut, Phellinus linteus facilitates their safe removal, supporting overall detoxification and digestive efficiency.
Scientific Articles on the Topic:
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC6572527/
https://faseb.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/epdf/10.1096/fj.201901943RR
Phellinus linteus Substances and Respiratory System:
The polysaccharides, particularly beta-glucans, play a pivotal role by activating macrophages and natural killer (NK) cells, which fortify the respiratory system's immune defenses against environmental challenges. These immune-enhancing compounds also help maintain a balanced response, preventing overactive inflammation that could harm lung tissues. Complementing this, triterpenoids exhibit anti-inflammatory properties that soothe the respiratory tract and modulate inflammatory pathways, ensuring tissue stability and reducing discomfort caused by environmental stressors.
Phenolic compounds act as powerful antioxidants, neutralizing free radicals that can damage lung cells and impair respiratory function. This oxidative stress reduction is further supported by trace minerals such as selenium and zinc, which are critical for enzymatic activities and antioxidant production, such as glutathione. These elements protect the delicate epithelial lining of the lungs, preserving its structure and function.
Additionally, Phellinus linteus contains ergosterol, a precursor to vitamin D, which supports adaptive immune function and enhances the respiratory system’s response to seasonal and environmental challenges. The combined action of these substances not only strengthens the lungs’ natural barriers but also aids in maintaining healthy oxygen exchange and tissue repair.
Scientific Articles on the Topic:
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC4022778/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC3769563/
Phellinus linteus Substances and Cardiovascular System:
Polysaccharides, particularly beta-glucans, play a crucial role in maintaining arterial flexibility and reducing inflammatory markers that can negatively affect vascular health. These compounds support balanced immune responses, ensuring that inflammation remains controlled without harming blood vessel function. Triterpenoids further contribute to cardiovascular wellness by protecting vascular tissues from oxidative damage and maintaining the structural integrity of blood vessels, which is essential for smooth blood flow.
Phenolic compounds act as potent antioxidants, neutralizing free radicals and safeguarding endothelial cells from oxidative stress. This protection reduces the risk of damage to lipids, which can otherwise lead to plaque buildup in arteries. Trace minerals such as selenium and zinc are integral to enzymatic processes that repair vascular tissues and produce antioxidants like glutathione, which shields heart and blood vessels from environmental and metabolic stressors. Additionally, ergosterol, a precursor to vitamin D, supports vascular health by aiding calcium regulation and ensuring proper blood vessel function.
By reducing oxidative stress, regulating inflammation, and protecting vascular integrity, Phellinus linteus promotes healthy circulation and efficient oxygen and nutrient delivery to the heart and other organs. These actions collectively enhance cardiovascular resilience, making the mushroom a valuable natural supplement for overall circulatory wellness.
Scientific Articles on the Topic:
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC7397296/
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC5378821/
Phellinus linteus Substances and Skin/Cellular Health:
Polysaccharides, particularly beta-glucans, play a vital role in improving skin hydration and elasticity by enhancing moisture retention and supporting collagen production. This helps maintain skin firmness and reduces the appearance of fine lines. Triterpenoids contribute by soothing irritation, balancing inflammatory responses, and protecting skin cells from environmental damage, such as pollutants and UV radiation, while strengthening the skin's natural barrier.
Phenolic compounds act as powerful antioxidants, shielding skin and cellular structures from oxidative stress that accelerates aging and cellular dysfunction. These antioxidants also aid in repairing damaged cells, preserving the integrity of skin layers and promoting a smooth, radiant complexion. Trace minerals like selenium and zinc support enzymatic processes crucial for cellular repair and regeneration, while also boosting the production of antioxidants like glutathione to defend skin cells against environmental and metabolic stressors. Additionally, ergosterol, a precursor to vitamin D, supports cell growth and differentiation, ensuring healthy skin turnover.
By reducing oxidative stress, enhancing cellular repair, regulating inflammation, and improving skin hydration, Phellinus linteus promotes youthful, resilient skin and robust cellular health. This holistic support makes it a valuable natural supplement for maintaining vibrant skin and optimal cellular function.
Scientific Articles on the Topic:
https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9587628/
https://www.jmb.or.kr/journal/download_pdf.php?doi=10.4014/jmb.1711.11043
https://www.nature.com/articles/ja201242
Phellinus linteus Substances and Nervous System:
Beta-glucans, a type of polysaccharide found in Phellinus linteus, foster a balanced immune response within neural tissues, which helps minimize inflammation and supports healthy nerve activity. Additionally, they contribute to improved neural communication by facilitating the production of essential signaling molecules. Complementing these effects, triterpenoids safeguard neurons by reducing oxidative stress and managing inflammation, thereby maintaining neural function and reducing risks of neurodegeneration.
Phenolic acids act as powerful antioxidants, neutralizing free radicals that can damage nerve cells and disrupt neural function. They also help protect the integrity of the myelin sheath and neuronal membranes. Trace minerals, such as selenium and zinc, are critical for processes like neurotransmitter synthesis and the repair of damaged neural tissues. These minerals also enhance the body’s antioxidant defenses by supporting the production of glutathione, which is essential for shielding neurons from oxidative damage. Meanwhile, ergosterol, a precursor to vitamin D, aids in neural growth, differentiation, and calcium balance, all of which are vital for effective neural transmission.
By minimizing oxidative stress, regulating inflammation, and supporting neural repair, Phellinus linteus plays a key role in strengthening the nervous system. This mushroom aids in preserving brain function, safeguarding neural connections, and promoting mental sharpness. Its comprehensive benefits make it an excellent natural option for enhancing cognitive performance and ensuring long-term neural health.
Scientific Articles on the Topic:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26773779/
https://www.jstage.jst.go.jp/article/jnsv/57/1/57_1_95/_pdf
Phellinus linteus Substances and Endocrine System:
Polysaccharides such as beta-glucans enhance immune balance and reduce inflammatory responses that can disrupt hormonal regulation, while also promoting efficient communication between glands and target tissues. Triterpenoids provide anti-inflammatory and antioxidative benefits, protecting the thyroid, adrenal glands, and pancreas from damage and ensuring consistent hormone production and secretion. Phenolic compounds act as powerful antioxidants, stabilizing glandular membranes and preventing oxidative damage to endocrine cells, preserving their long-term functionality.
Trace minerals, including selenium and zinc, are critical for enzymatic processes involved in hormone synthesis, such as thyroid hormones and insulin, and help detoxify endocrine tissues from environmental and metabolic stressors. Ergosterol, a precursor to vitamin D, supports calcium regulation and cellular differentiation, aiding in the balance of hormones related to bone health and metabolism.
Through the combined actions of its bioactive components, Phellinus linteus reduces oxidative stress, modulates inflammation, repairs glandular tissues, and ensures a steady release of hormones. These processes maintain endocrine system efficiency and metabolic harmony, making this mushroom a valuable natural ally for promoting balanced hormonal function and overall endocrine health.
Scientific Articles on the Topic:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35079934/
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0141813024008651
https://www.mdpi.com/2072-6643/11/2/296
Recommended Dosage
The optimal dosage of Phellinus linteus depends on its form and the individual’s health goals. Below are general guidelines:
Extracts (Liquid or Powdered):
Dosage: 500 mg to 1,000 mg per day of concentrated extract (standardized to key bioactive compounds like polysaccharides).
Liquid extracts are often dosed at 1–2 ml, taken 1–3 times daily.
Capsules/Tablets:
Dosage: 1–2 capsules (usually 500 mg each) per day, as indicated by the manufacturer.
Decoctions (Traditional Tea Preparation):
Dosage: 5–10 grams of dried mushroom per day, boiled for 30–60 minutes to make a medicinal tea.
It is recommended to start with a lower dosage and gradually increase as needed, under the guidance of a healthcare provider.
Best Time to Take Phellinus linteus
Morning: Taking Phellinus linteus in the morning is beneficial for those seeking its immune-boosting and energy-enhancing effects, as it supports the body’s natural rhythm.
Evening: For its adaptogenic and calming properties, it can also be taken in the evening to promote relaxation and cellular repair during sleep.
Before or After Meals
Before Meals: Phellinus linteus is best taken on an empty stomach to maximize absorption of its bioactive compounds, especially polysaccharides and triterpenoids. This ensures efficient delivery to the body’s systems.
After Meals: For individuals with sensitive stomachs, taking it after meals may help reduce any gastrointestinal discomfort.
Contraindications
While Phellinus linteus is generally considered safe for most people, there are certain circumstances where caution is advised:
Pregnancy and Breastfeeding: There is insufficient evidence to confirm safety during pregnancy or breastfeeding. Consult a healthcare provider before use.
Autoimmune Conditions: Individuals with autoimmune disorders (e.g., lupus, rheumatoid arthritis) should use caution, as Phellinus linteus may stimulate immune activity.
Bleeding Disorders: As it may have mild blood-thinning effects, those with bleeding disorders or scheduled surgeries should avoid its use.
Interactions with Other Products or Substances
Phellinus linteus is generally well-tolerated, but potential interactions should be considered:
Medications:
Anticoagulants or Antiplatelets: Phellinus linteus may enhance the effects of blood-thinning medications like warfarin, increasing the risk of bleeding.
Immunosuppressants: As it modulates immune activity, it may counteract medications used to suppress the immune system.
Supplements:
Other Adaptogens: When combined with other adaptogens like reishi or ashwagandha, the effects on immune modulation and stress balance may be amplified.
Antioxidants: Combining with antioxidant-rich supplements, such as vitamin C, may enhance its oxidative stress-reducing benefits.
Caffeine: Phellinus linteus may complement caffeine's energy-boosting effects by reducing oxidative stress, but excessive stimulation should be monitored.
Conclusion:
From enhancing immune function and supporting digestive health to promoting respiratory efficiency, cardiovascular wellness, and cellular vitality, Phellinus linteus demonstrates its versatility as a natural supplement. Additionally, its ability to protect neural pathways and regulate hormonal balance highlights its profound impact on nervous and endocrine systems. With its holistic and scientifically supported benefits, Phellinus linteus continues to gain recognition as a valuable natural ally for maintaining overall wellness and vitality.