Botanical Characteristics
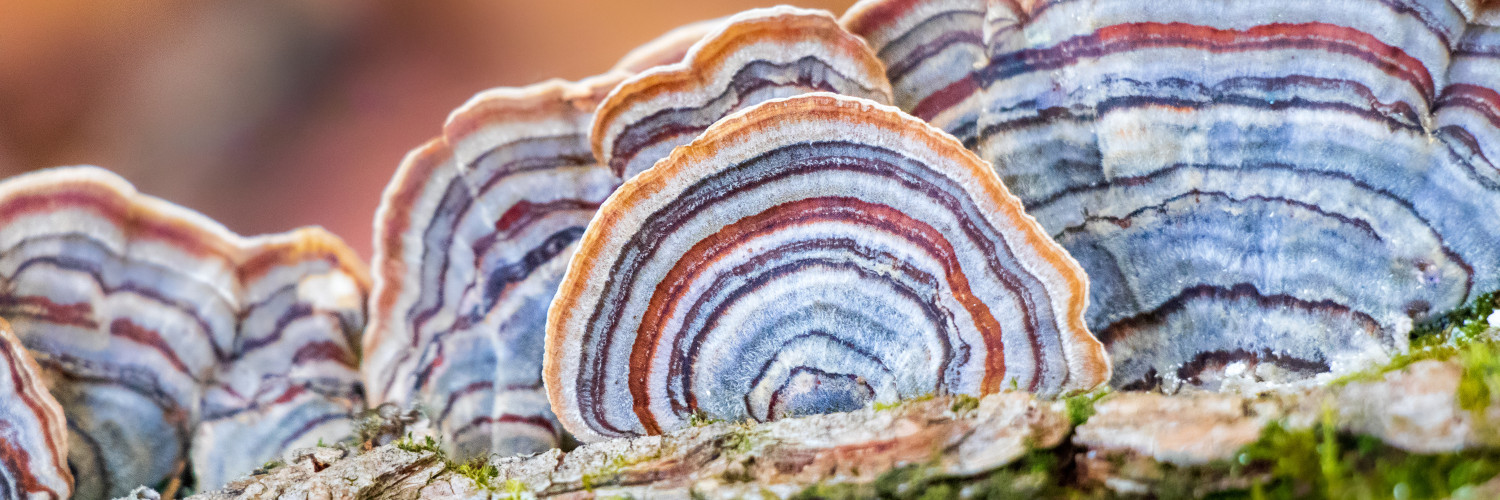
Turkey Tail, scientifically known as Trametes versicolor, is a polypore mushroom characterized by its vibrant, fan-shaped caps. The caps display a wide array of colors, typically featuring concentric zones of different hues such as brown, orange, white, and blue, which resemble a wild turkey's tail feathers. This mushroom has a tough and leathery texture, with a white, porous underside where spores are released. Its fruiting body is usually 1-3 cm in width and grows in overlapping clusters on decaying wood.
Habitat and Growth Features
Turkey Tail mushrooms are widely distributed across the globe, thriving in diverse climates from tropical to temperate regions. They predominantly grow on dead or decaying hardwood trees such as oak, maple, and beech. These fungi play a crucial role in the ecosystem by decomposing wood, recycling nutrients back into the soil. Turkey Tail mushrooms prefer moist, shaded environments and can be found throughout the year, especially during the fall and spring seasons.
Chemical Composition
Turkey Tail mushrooms are rich in a variety of bioactive compounds. Some of the key components include:
Polysaccharide-K (PSK) and Polysaccharopeptide (PSP): These are unique protein-bound polysaccharides known for their beneficial properties.
Beta-glucans: Complex sugars that support various bodily functions.
Antioxidants: Compounds such as phenols and flavonoids that help protect cells from damage.
Triterpenoids: Compounds that support bodily processes.
History of Usage
The use of Turkey Tail mushrooms dates back centuries, particularly in traditional Chinese and Japanese practices. Known as "Yun Zhi" in Chinese, these mushrooms have been used to support various aspects of well-being. In Japan, the extract called "Krestin" has been studied extensively for its beneficial properties. Historical texts and records reveal that Turkey Tail was valued not only for its wellness-promoting attributes but also for its ability to enhance vitality and resilience.
Turkey Tail (Grifola frondosa) Supports:
- Immune System
- Digestive System
- Respiratory System
- Antioxidant System
- Liver Health
Turkey Tail Substances and Immune System Support
Turkey Tail (Trametes versicolor) supports the immune system through its bioactive compounds, primarily polysaccharides like Polysaccharide-K (PSK) and Polysaccharopeptide (PSP). These polysaccharides enhance immune function by stimulating macrophages, natural killer (NK) cells, and T-lymphocytes, which are crucial for the body's defense mechanisms. PSK boosts the activity of macrophages and NK cells, while PSP increases the production and activity of T-lymphocytes, ensuring a balanced immune response.
Additionally, Turkey Tail contains antioxidants such as phenols and flavonoids, which protect immune cells from oxidative stress, further supporting immune health. Clinical studies have demonstrated that regular consumption of Turkey Tail extracts can enhance immune surveillance and response, making it a valuable dietary supplement for maintaining immune health.
In summary, Turkey Tail mushroom supports longevity through immune enhancement, antioxidant protection, and promoting metabolic health, contributing to an overall increase in lifespan and well-being.
Scientific Articles on the Topic:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6889544/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4684115/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6010034/
Turkey Tail Substances and Digestive System Support
A key component of Turkey Tail's beneficial profile is its high polysaccharide content, particularly Polysaccharopeptide (PSP) and Polysaccharide-K (PSK). These compounds are known for their ability to support the normal functioning of the digestive system. They work by enhancing the gut microbiome, promoting the growth of beneficial bacteria. This improved microbial balance aids in the efficient breakdown and absorption of nutrients, fostering a more robust digestive process.
Turkey Tail's anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties play a crucial role in maintaining a healthy digestive system. Turkey Tail helps soothe the digestive tract lining, reducing discomfort and promoting overall gut health. Its antioxidants combat oxidative stress, protecting digestive tissues and ensuring their optimal function.
Turkey Tail is also a good source of dietary fiber, which is essential for maintaining regular bowel movements. The fiber content adds bulk to the stool, facilitating its passage through the digestive tract and ensuring regularity.
Scientific Articles on the Topic:
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25006989/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5618583/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5302426/
Turkey Tail Substances and Respiratory System Support
Research indicates that the polysaccharides in Turkey Tail can aid in the repair and regeneration of lung tissues. This is particularly beneficial for individuals exposed to environmental pollutants or those recovering from respiratory issues. The regenerative properties help maintain lung elasticity and function, ensuring efficient respiratory performance.
Turkey Tail's anti-inflammatory compounds, such as polysaccharopeptides (PSP) and polysaccharide-K (PSK), help to support the respiratory tract. These substances support clear airways and ease breathing.
The mushroom is rich in antioxidants, including phenols and flavonoids, which combat oxidative stress in the respiratory tract. Oxidative stress can lead to impaired respiratory function. The antioxidant compounds in Turkey Tail help neutralize free radicals, thereby protecting respiratory tissues and supporting overall lung health.
Scientific Articles on the Topic:
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25784670/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2772753X22000120
Turkey Tail Substances and Antioxidant System Support
Phenolic compounds in Turkey Tail mushroom, such as quercetin and baicalein, play a pivotal role in its antioxidant activity. These compounds act as electron donors, which is crucial for stabilizing free radicals. Free radicals are unstable molecules that can cause significant cellular damage. By donating electrons, quercetin and baicalein neutralize these free radicals, preventing them from interacting with and damaging vital cellular components such as DNA, proteins, and lipids.
Additionally, these phenolic compounds have the ability to regenerate other antioxidants, such as vitamin C and vitamin E, which are vital for maintaining the body's overall antioxidant capacity. This regeneration process ensures that the body has a sustained supply of antioxidants to continuously combat oxidative stress.
Flavonoids in Turkey Tail, including myricetin and catechin, also contribute significantly to its antioxidant effects. These flavonoids scavenge free radicals directly, meaning they actively seek out and neutralize these harmful molecules. Beyond direct scavenging, myricetin and catechin chelate metal ions, such as iron and copper, which catalyze the formation of free radicals through Fenton reactions. By binding to these metal ions, flavonoids prevent them from participating in these reactions, thereby reducing the overall production of free radicals.
Furthermore, flavonoids enhance the body's internal antioxidant defense by upregulating the production of key antioxidant enzymes, such as superoxide dismutase (SOD) and glutathione peroxidase. These enzymes play crucial roles in neutralizing superoxide radicals and hydrogen peroxide, respectively, which are common reactive oxygen species in the body. By boosting the activity of these enzymes, flavonoids help maintain a robust antioxidant defense system, protecting cells and tissues from oxidative damage.
Scientific Articles on the Topic:
Turkey Tail Substances and Liver Health
Polysaccharopeptides (PSP) and Polysaccharide-K (PSK) exhibit strong antioxidant properties, neutralizing free radicals and reducing oxidative stress on liver cells, thereby preventing cellular damage and maintaining liver function.
Bioactive compounds in Turkey Tail assist the liver's detoxification processes by enhancing its ability to filter and eliminate toxins from the body. Additionally, beta-glucans present in Turkey Tail help reduce liver inflammation, which can otherwise lead to chronic conditions.
By mitigating inflammatory responses, these compounds support the maintenance of healthy liver tissue. Through these combined actions, Turkey Tail mushroom substances contribute significantly to liver health, protecting liver cells, enhancing immune function, supporting detoxification, and reducing inflammation.
Scientific Articles on the Topic: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6270077/
Usage Guidelines for Turkey Tail Mushroom
Recommended Dosage
The typical recommended dosage for Turkey Tail mushroom extract is 1,000 to 3,000 mg per day. It is advisable to start with a lower dose and gradually increase it to the desired amount based on individual tolerance and response.
Best Time to Take
Before Meals: For optimal absorption and effectiveness, take Turkey Tail mushroom extract before meals. Taking it on an empty stomach allows for better absorption of its bioactive compounds and prepares the digestive system for nutrient assimilation.
Contraindications and Precautions
Allergies: Individuals with known allergies to mushrooms should avoid Turkey Tail mushroom extract.
Immune System Disorders: People with autoimmune diseases or those taking immunosuppressive drugs should consult a healthcare provider before using Turkey Tail, as it may modulate immune function.
Pregnant or Breastfeeding Women: It is advisable for pregnant or breastfeeding women to consult with a healthcare provider before taking Turkey Tail mushroom extract.
Surgery: Due to its potential immune-modulating effects, discontinue use at least two weeks prior to scheduled surgery.
Interactions with Other Products or Substances
Immunosuppressive Medications: Turkey Tail may interact with medications that suppress the immune system, potentially reducing their effectiveness.
Anticoagulant or Antiplatelet Drugs: As with many supplements, it is important to exercise caution when taking Turkey Tail with blood-thinning medications, as there might be an increased risk of bleeding.