Botanical Characteristics
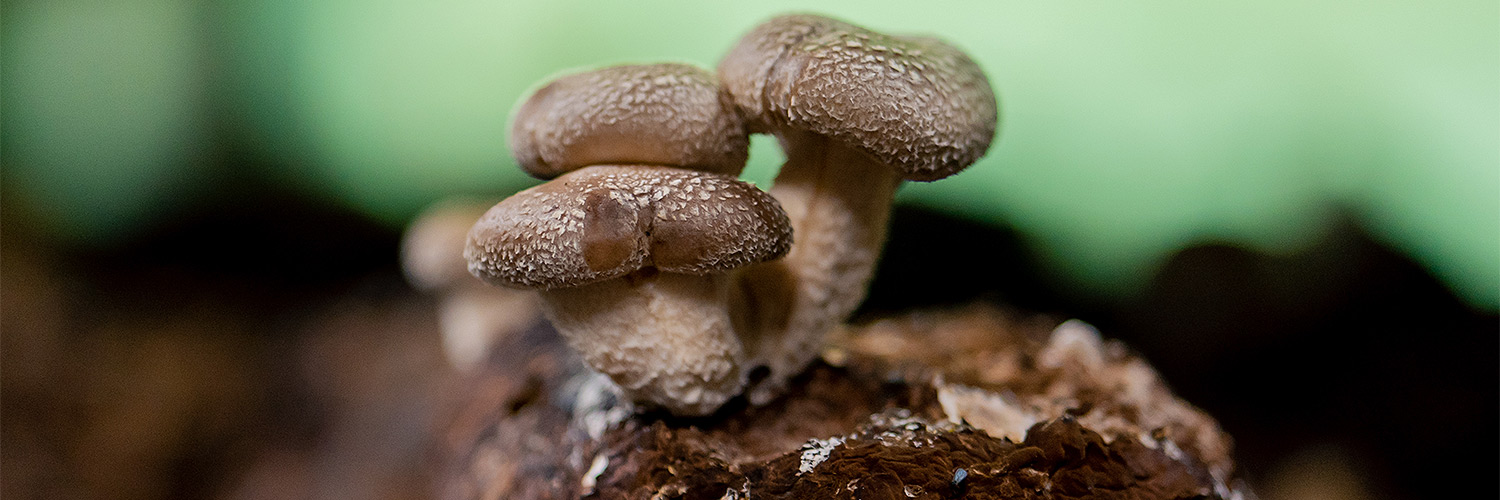
Shiitake mushrooms, scientifically known as Lentinula edodes, are distinguished by their umbrella-shaped caps that range in color from light to dark brown. The caps can grow up to 10 cm in diameter and have a smooth, slightly cracked texture. The gills beneath the cap are white, and the stem is fibrous, typically lighter than the cap. These mushrooms are saprotrophic, primarily growing on the decaying wood of hardwood trees.
Chemical Composition
Shiitake mushrooms are rich in a variety of bioactive compounds. Key components include polysaccharides like lentinan, beta-glucans, eritadenine, and various sterols. They also contain essential amino acids, vitamins such as B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), D, and minerals including zinc, selenium, and copper. The presence of antioxidants and other phenolic compounds contributes to their beneficial properties.
Habitat
Native to East Asia, Shiitake mushrooms naturally thrive in warm, moist climates. They grow predominantly on the decaying logs of hardwood trees such as oak, chestnut, and beech. In controlled environments, they are cultivated on synthetic logs made from sawdust and other organic materials. The optimal growth conditions include high humidity and temperatures ranging between 20°C to 28°C.
Taste
Shiitake mushrooms are prized for their rich, umami flavor, which is often described as savory and slightly earthy. This unique taste makes them a popular ingredient in various culinary dishes around the world. When dried, their flavor becomes more intense, making them a versatile component in soups, stews, and sauces.
History of Use
The history of Shiitake mushrooms dates back over a thousand years, primarily in China and Japan. They were first cultivated in China during the Song Dynasty (960-1279 AD) and have since been highly valued not only for their culinary uses but also for their perceived beneficial properties. In traditional Chinese and Japanese cultures, Shiitake has been used in various forms, including dried, fresh, and as an extract. Today, they are globally recognized and extensively studied for their potential wellness benefits, contributing to their widespread popularity in modern cuisine and dietary supplements.

Shiitake Mushroom (Lentinula edodes) Extract Benefits:
- Immune System
- Cardiovascular System
- Skeletal System
- Digestive System
- Integumentary System (Skin)
- Nervous System
- Endocrine System
- Circulatory System
Shiitake Substances and Immune Function Support
Beta-glucans, found in abundance in Shiitake mushrooms, are known to enhance the immune response by activating immune cells such as macrophages, natural killer cells, and T-cells. These immune cells play a crucial role in identifying and eliminating pathogens, thereby improving the body's ability to resist infections. Lentinan, a specific type of beta-glucan unique to Shiitake, has been extensively studied for its immunomodulatory properties. It stimulates the production of cytokines, which are essential for cell signaling in immune responses, further enhancing the body's defense mechanisms.
In addition to polysaccharides, Shiitake mushrooms contain essential vitamins and minerals that contribute to a well-functioning immune system. Vitamins such as B2 (riboflavin), B3 (niacin), and D, along with minerals like zinc and selenium, support various aspects of immune function. For instance, vitamin D is crucial for the activation of immune defenses, while zinc and selenium are known for their roles in maintaining immune cell function and reducing oxidative stress, respectively.
In conclusion, the diverse array of bioactive compounds in Shiitake mushrooms synergistically supports immune function by enhancing the activity of immune cells, promoting the production of vital cytokines, and providing essential nutrients that bolster overall immune function. Regular consumption of Shiitake mushrooms can be a valuable addition to a diet aimed at maintaining and enhancing immune function.
Scientific Articles on the Topic: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/25866155/
Shiitake Substances and Cardiovascular Function Support
These mushrooms contain an array of bioactive compounds, including eritadenine, beta-glucans, and various polysaccharides, which collectively support cardiovascular function through multiple mechanisms. Eritadenine is particularly noted for its ability to influence lipid metabolism, thereby assisting in the maintenance of normal cholesterol levels. Beta-glucans, soluble fibers found in shiitake, are instrumental in promoting normal blood pressure and improving lipid profiles.
Additionally, shiitake mushrooms are rich in antioxidants, such as selenium and vitamins, which help combat oxidative stress, a key factor in cardiovascular challenges. These antioxidants neutralize free radicals, thereby supporting the integrity of blood vessels and reducing the risk of arterial damage. Shiitake mushrooms also contribute to cardiovascular wellness through their irritation-soothing properties, helping to maintain a balanced response to irritation in the cardiovascular system.
Furthermore, the presence of bioactive polysaccharides in shiitake supports normal endothelial function, promoting vascular flexibility and normal blood flow. Regular inclusion of shiitake in the diet, either through whole mushrooms or supplements, can thus play a beneficial role in supporting overall cardiovascular function. This multifaceted support underscores shiitake mushrooms' potential as a valuable addition to dietary regimens aimed at maintaining cardiovascular wellness.
Scientific Articles on the Topic: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6302894/
Shiitake Substances and Skeletal Function Support
Rich in essential nutrients, shiitake mushrooms contain significant amounts of vitamin D, which is crucial for calcium absorption and bone mineralization. The presence of vitamin D in shiitake mushrooms can help maintain optimal bone density and promote overall bone strength.
Additionally, shiitake mushrooms are a source of important minerals such as zinc, magnesium, and selenium, which play vital roles in bone metabolism and the maintenance of a normal skeletal system. These minerals are essential for the proper functioning of osteoblasts and osteoclasts, the cells responsible for bone formation and resorption, respectively. By supporting these cellular functions, shiitake mushrooms contribute to the dynamic process of bone remodeling and repair.
Shiitake mushrooms also contain polysaccharides, such as beta-glucans, which have been shown to have potential bone-protective effects. These polysaccharides may enhance bone formation and inhibit bone resorption, further contributing to skeletal function.
The antioxidants present in shiitake mushrooms, including selenium and various vitamins, help protect bone cells from oxidative damage, thereby preserving bone structure and function. Regular consumption of shiitake mushrooms, either as part of a balanced diet or through supplements, can thus play a beneficial role in supporting skeletal function.
Scientific Articles on the Topic:
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5214552/
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0022316622024543
Shiitake Substances and Digestive Function Support
These mushrooms are an excellent source of dietary fiber, particularly beta-glucans, which play a critical role in promoting regular bowel movements and maintaining gut function. The fiber content in shiitake mushrooms aids in the efficient digestion of food, enhances nutrient absorption, and supports a normal gut microbiome by serving as a prebiotic, fostering the growth of beneficial gut bacteria.
Furthermore, shiitake mushrooms contain polysaccharides, such as lentinan, which contribute to a balanced digestive system. These compounds support the body's natural digestive processes and help maintain the integrity of the gut lining. The presence of enzymes in shiitake mushrooms also assists in the breakdown of complex carbohydrates, proteins, and fats, facilitating smoother digestion.
In addition to fiber and polysaccharides, shiitake mushrooms are rich in antioxidants, such as selenium and vitamins, which protect the digestive tract from oxidative stress caused by free radicals.
Moreover, shiitake mushrooms possess soothing properties that can contribute to a calmer and more stable digestive environment, enhancing overall digestive comfort.
Regular inclusion of shiitake mushrooms in the diet , whether through whole mushrooms or supplements, can thus play a beneficial role in supporting digestive function. This multifaceted support underscores the potential of shiitake mushrooms as a valuable addition to dietary regimens aimed at promoting a normal and efficient digestive system.
Scientific Articles on the Topic: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9751717/
Shiitake Substances and Skin Function Support
These mushrooms are rich in antioxidants, including selenium, vitamin D, and various polyphenols, which protect the skin from oxidative stress and environmental damage. By neutralizing free radicals, these antioxidants help prevent premature aging, reduce the appearance of fine lines and wrinkles, and maintain overall skin vitality.
The polysaccharides found in shiitake mushrooms, particularly beta-glucans, are known for their hydrating properties, helping to retain moisture in the skin and improve its elasticity. These compounds also support the skin's natural barrier function, keeping it resilient against environmental aggressors and reducing the risk of dryness and irritation. Furthermore, beta-glucans have been shown to promote skin regeneration, making shiitake mushrooms beneficial for maintaining a normal and youthful complexion.
Shiitake mushrooms also contain kojic acid, a natural compound that helps to even out skin tone. Kojic acid inhibits the production of melanin, the pigment responsible for dark spots and uneven skin tone, thereby promoting a more radiant and uniform complexion.
Regular use of shiitake mushroom extracts in skincare routines, whether through topical applications or dietary supplements, can thus play a beneficial role in supporting skin function.
Scientific Articles on the Topic: https://www.mdpi.com/2079-9284/3/3/22
Shiitake Substances and Nervous Function Support
Shiitake mushrooms contain a variety of bioactive compounds, including polysaccharides, beta-glucans, and eritadenine, which collectively contribute to the maintenance and enhancement of nervous system function.
Polysaccharides and Beta-Glucans, found abundantly in shiitake mushrooms, are known for their immunomodulatory and neuroprotective properties. They help in maintaining the integrity of nerve cells and promoting the repair of damaged nerves, thus supporting the nervous system's resilience and function.
Eritadenine in shiitake mushrooms plays a crucial role in maintaining neural function by supporting the metabolism of lipids and enhancing circulation, which is vital for optimal brain function. Improved blood flow ensures that nerve cells receive adequate nutrients and oxygen, facilitating better cognitive performance and mental clarity.
Shiitake mushrooms are rich in antioxidants, which help protect nerve cells from oxidative stress. This protection is critical for preventing neurodegeneration and maintaining normal neural pathways, contributing to better memory and cognitive functions.
Compounds in shiitake mushrooms can promote the production of neurotrophic factors, which support the growth, survival, and differentiation of neurons. This helps in sustaining neural plasticity, essential for learning and memory.
Regular intake of shiitake mushroom extracts supports overall mental well-being and maintains a balanced mood by modulating neurotransmitter levels.
Scientific Articles on the Topic: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1756464620305508
Shiitake Substances and Endocrine System Support
Endocrine glands, which secrete hormones directly into the bloodstream, play a crucial role in regulating various body functions including metabolism, growth, and reproduction.
Polysaccharides and Beta-Glucans are known for their immune-modulating properties, which indirectly support the endocrine system by maintaining overall body homeostasis. The immune system and endocrine system are closely linked, and a balanced immune response can positively influence endocrine function.
Eritadenine found in Shiitake mushrooms may help in regulating lipid levels and promoting cardiovascular function, which is intrinsically connected to endocrine function, particularly the hormones related to metabolism.
As a powerful beta-glucan, lentinan has been researched for its role in enhancing immune function, which can support endocrine balance. By aiding the immune system, lentinan helps in maintaining the optimal functioning of the endocrine glands.
Additionally, Shiitake mushrooms contain essential vitamins and minerals such as B vitamins, selenium, and zinc, which are crucial for the production and regulation of hormones. These nutrients support various endocrine glands, including the thyroid, adrenal glands, and pancreas, promoting overall hormonal balance.
Usage Guidelines for Shiitake Extract in Plant-Based Vegetarian Capsules
How to Use Shiitake
With Water or Beverage: Take the capsules or powdered extract with a glass of water or your preferred beverage.
Timing: It's advisable to take the capsules at the same time each day to maintain consistent levels in your body. Morning or mid-morning intake is often recommended to align with your body's natural rhythm.
With or Without Food: Shiitake extract capsules can be taken with or without food. However, if you experience any digestive discomfort, consider taking them with a meal.
Contraindications
Allergies: Avoid use if you have a known allergy to mushrooms.
Pregnancy and Nursing: If you are pregnant, nursing, or planning to become pregnant, consult a healthcare provider before using this supplement.
Immune System Modulation: Shiitake extract may stimulate the immune system. Individuals with autoimmune conditions should use caution as it may exacerbate their condition. Consultation with a healthcare provider is recommended.
Bleeding Disorders: Shiitake extract has been associated with anticoagulant effects, which may increase the risk of bleeding. Individuals with bleeding disorders or those taking anticoagulant medications should avoid using shiitake extract or use it under strict medical supervision.
Digestive Sensitivity: Some individuals may experience digestive discomfort when taking shiitake extract. If you have a history of gastrointestinal issues, start with a lower dose to assess tolerance and consult a healthcare provider if symptoms persist.
Medication Interactions
Immunosuppressants: Shiitake extract may interact with immunosuppressive drugs, potentially reducing their effectiveness. Individuals taking immunosuppressants should consult their healthcare provider before using shiitake extract.
Blood Thinners: As mentioned earlier, shiitake extract may enhance the effects of blood-thinning medications, increasing the risk of bleeding. Those on blood thinners should seek medical advice before use.